Italian members of the secret society of the "Carbonari" of the 19th century. They may be planning a revolution or maybe a pizza party. Is this our future?
Many ideas are floating in the memesphere on how to survive the current situation. Some people think of moving to a country ruled by less dangerous governments, others of retreating to an agricultural village in some remote area, and others about the possibility of going undercover. That is, disappearing from the sight of the government, waiting for better times that might come in the future. And even acting to bring those times closer.
Is it possible? Could you really hide in a world that's becoming more and more like the fabled "panopticon," a prison where the jailers have a full view of everything that the prisoners do? Difficult, surely, but it is also true that we still maintain a certain degree of freedom inside our brains, provided that we don't expose them to government propaganda. So, could people who think alike in certain matters get together and form a secret network?
As you can imagine, it is not an easy task, and it may also be dangerous. When we think of a secret organization, we think of something like the famed Al-Qaeda society. They managed to carry out one of the most successful terrorist attacks in history and, remarkably, they did so while leaving no traces anywhere, except for a videocassette tape showing a bearded sheik in a cave accusing himself of having been the perpetrator.
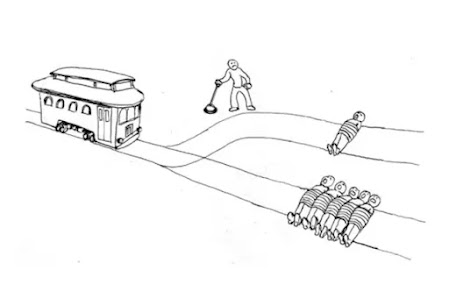
The problem with discussing secret societies is that, obviously, they are secret. That means we know something only of the ones which were not so successful at keeping their secrecy. In any case, it seems that secret societies are typically based on a pyramidal cell structure, where each member knows only the members of his/her cell (typically no more than three). The reason for this structure is the need to minimize the effect of treason: any member can defeat and betray the others, but the smaller the number of members he/she knows, the smaller will be the damage. You can find a good description of how cell-based secret societies are supposed to work in terms of keeping secrecy in the novel by Robert A. Heinlein, "The Moon is a Harsh Mistress" (1966) (*). Similar descriptions exist all over the Web.
A cell-based structure is well-known, but it is not very practical. One problem is that it grows very slowly. If you want to have at least a few thousand people in the pyramid, probably the minimum needed to start a serious revolution, with cells of three people, you need at least 6-7 layers. That makes no sense: an order coming from the top must go through each step before it arrives at the base layer, where it can be finally carried out. If a structure like this one were ever to work for real, cells would have to be much larger.
Even so, a cell structure is not a good idea in terms of generating a revolution. Nobody would want to join an organization so secretive that they would never be able to know who is at the top. People need leaders to act, and they need to know who their leaders are. But being a member of a small revolutionary cell freezes you in a closed world where you can only follow orders coming from above, together with just a few like-minded companions. Why should you do that? For some lofty ideal? Maybe, but how do you know that your leaders are actually working for those ideals? How do you know that the organization has not been infiltrated by your enemies? Or by aliens from Betelgeuse?
In practice, cell-based secret organizations can work only as military covert operations, as you may discover if you take up a career as a spy. But, typically, people who take up spying do that for money which, indeed, is what keeps together the organization. The carrot is normally coupled with a massive stick: if you betray, you risk your life: either you will be hanged as a spy, or shot as a traitor by other members of the organization. I don't know how much spies are paid, but I think it is not a condition anyone would want to find themselves in.
Can we think of more effective ideas? Yes, but we have to accept that the organization cannot be 100% secret, and neither it should be. Early Christianity is a good example of a semi-secret organization that was created in opposition to an oppressive government. A common legend has that the early Christians would hide in subterranean refuges called "catacombs." But these were never secret places (hiding in caves seems to be only a habit of bearded sheiks in Afghanistan). The historical catacombs were just cemeteries. But it is true that many Christians kept a low profile in a society that sanctioned their beliefs with death. Later, the Muslims practiced the Taqiya, a precautionary dissimulation in the face of persecution.
Both Christianity and Islam were successful, although only in the long run, and not without a harsh struggle. So, it is possible to fight oppression by a religion. You could even think of creating a new one, it is probably possible in the US. For those of us who think that the task is a little too steep, though, we may need a different approach. Can we think of non-religious groups that could successfully oppose state oppression? There are some examples in history, one is that of the Carbonari, who were most active in the 1800s, in Italy and in other European countries.
The story of the
Carbonari is as fascinating as it is scarcely known. They started around 1800 as liberals who hated all forms of oppression. They were anti-clerical, wanted to destroy the Catholic Church, and aimed at a revolution to get rid of the many petty monarchies that ruled the Italian peninsula. They were not necessarily favorable to a united Italy, although it must have been clear to them that it was an unavoidable consequence of the elimination of the local tyrants.
As a political movement, the
Carbonari were not very successful. They tried an Italy-wide
revolution in 1820, but they failed. Over the years, they were replaced by more open organizations, such as the "
Giovine Italia" (Young Italy) created by a former
Carbonaro, the Italian intellectual Giuseppe Mazzini. Yet, we cannot say that the Carboneria was a failure. It was alive (and heavily repressed) during the Fascist period in Italy, and it was still playing a role in Italy in the 1970s, as a group of members of the Italian Republican Party. Some say they still exist, surely a legend but, who knows? In any case, the term "
carboneria" is still used in Italy to indicate groups of people acting in partial or total secrecy. (do not confuse it with the
carbonara, a pasta dish!)
So, what was the Carboneria, exactly? It was an offshoot of a burst of semi-secret societies that appeared at the end of the 18th century. The Freemasons are probably the oldest, there followed others with different names: the "Adelphians," ("brothers") the "Philadelphians," and more. The Carbonari were the Italian version of this movement of ideas that aimed at removing the old European ruling class, the landed nobility. The idea was to replace them with the entrepreneur class, a dynamic economic force that was growing on the availability of cheap energy from coal. This class took power in France with the French Revolution of 1789, and it advanced in Europe with a series of local revolutions, then with Napoleon and his heirs.
The name "Carbonari" means 'charcoal makers.' The choice of this name goes in parallel with the older idea of Freemasonry. The Freemasons emphasized the knowledge of their members as "masons" -- people who knew how to design and build structures and so were independent of the rule of the nobles. The Carbonari, instead, focused on the technical prowess of the people who could make charcoal from wood. The "carbonaro" was idealized as an independent person who could make a living out of his knowledge and skills and would not accept being oppressed by anyone, including the government.
A point that made the Carboneria successful was that it was never a completely secret society. Indeed, most of what we know about the Carbonari comes from police reports. They knew who the Carbonari were and probably preferred to leave them relatively in peace rather than force them to go into true secrecy. From these reports, we know something about their rituals. Here is an example from
a document of 1818, describing the ceremony of acceptance of a new member.
Grand Master - What do you ask, Pagan?
He answers: the light.
Gr. M. - This will be granted to you at the third blow of my hatchet.
The Assistants turn their hatchets against him. The Master of Ceremonies takes off his blidfold.
Gr. M. - These hatchets, which you see in our hands, will be used to kill you in case of perjury on your part. On the contrary, they will fly to your aid if you need them,
The Master of Ceremonies leads him to the Throne.
You must pronounce again and ratify a part of the Oath you swore blindfolded. Repeat with me: I swear and promise to recognize and observe the General Statutes and Regulations of the Carbonic Order and of the High Sale of Naples and those no less of this Respectable Sale of which I am a Member.
That said, the Baptism of the Initiate happens, which is done as follows:
The Grand Master touches his eyes, ears, nostrils and lips with a linen cloth slightly wet in water, saying afterwards:
- You shall not see except by our eyes.
- You will not hear except by our ears.
- You shall smell the effluvia of our coal.
- You will speak only wise words.
Having said this the Grand Master continues:- To the glory of the Grand Master of the Universe, in the name of Saint Theobald and under the auspices of the High Sale of Naples, by the powers confided to me, I constitute you an Apprentice Carbonaro and a Member of this Respectable Sale.
(He rises and gives him the decorations).
I know that it sounds like the Simpsons' episode of the "
Stonecutters" and that is because the episode was created specifically to reflect the way these semi-secret societies work. But if you imagine the ceremony taking place in some secret place, maybe a shack in the woods at night, then it must have been quite impressive. The idea was to generate fealty bonds among members by creating an elaborate symbolism and word codes supposed to be known only by initiates. For instance, a local
carbonari association was called a "
Vendita" (sale), the reunions were held in a "
Baracca" (shack), the aspiring members were called "
Pagani" (Pagans), and so on. It worked reasonably well if the Carboneria thrived and survived for so long.
So, the question is: could we create a new Carboneria, today? And would it be useful for something? Maybe the answer is positive to both questions, but we need to be aware of the limits of what can be done. Essentially, as the Carbonari learned, you cannot hope to obtain and maintain real secrecy. If you strive for it too hard, not only you'll fail, but you'll make yourself suspect. Even if you don't do anything illegal, never forget that governments are constantly looking for people to blame for their own failures -- scapegoats. And when they find a suitable target, they have no scruples. That is, unless you have the power and the money to create a true secret society to take over the state. It has happened many times in history (**), and it will surely happen again (it may already have happened). But, in this case, it is unlikely that you would be interested in this post -- you already know enough on the matter.
What you can do is play the game relatively in the open. In most Western states, it is perfectly legitimate to form associations, formal or informal, that pursue some goal that may be weird, but not illegal. For instance, it is perfectly legal to believe that the Earth is flat and to form an association of believers. It actually exists (the Flat Earth Society, FES) and may have several thousand members. It is normally dismissed as a group of slightly feebleminded people. But ask yourself a question: could the FES be the front of an association that has entirely different purposes? Imagine that the core members are Aliens planning to exterminate humankind, how would you know? Then, of course, the group would be formed of an outer "ring" of true believers and an inner ring of initiates who actually know that they are servants of the Green Oozing Aliens from Betelgeuse and that they are bound to feed to their masters one baby to eat every week.
So, you can shroud your group with some harmless or weird purposes that will not attract too much attention from the powers that be. Then, there remains the problem of how the members will actually know what the society is about. That becomes a question of communication, and communication always involves codes. Again, you have to be cautious: all codes can be cracked. More than that, the very fact of using codes makes the users suspicious. That's especially true if you use the Internet, as you obviously must do. Some people use special precautions for their everyday communications, things like encoded messages, hidden servers, all that. Maybe is a good idea, but I am not sure. The more you try to hide, the more suspicious you look to the powers that be. The problem can be circumvented, in part, by using the technique called "steganography" which consists in utilizing terms or objects as symbols with a hidden meaning. So, if you agree with your follower that the term "lawyer" means "Alien from Betelgeuse," then an innocent sentence that goes as, "let's go meet our lawyers" carries a meaning that the non-initiate cannot decipher. There are limits to what steganography can do, but it can be extremely effective.
In the end, what's realistically possible for a
carbonaro of modern times? We are going through enormous changes, and we simply don't know what shape a future society will take. If we don't go back to the Middle Ages (or to hunting and gathering), what role will have governments in the future? Will there
exist governments? How will the internet be shaped? As a centralized entity managed by hordes of fact-checkers? Or by a large number of "rings" of like-minded people who speak mainly to each other? For the time being,
a blog with a funny title that mentions an ancient Roman Philosopher may be seen as the equivalent of a
vendita carbonara, not a secret place, but a
baracca where the adepts don't do so much damage that they deserve active repression. So far, at least...
_____________________________________________________________
(*) From "The Moon is a Harsh Mistress" - By Robert A. Heinlein (1966)
Dialog of the three of the protagonists, professor Bernardo de La Paz (Prof.), Wyoming Knott ("Wyo") and Manuel Garcia O'Kelly-Davis (Mannie) (speaking voice)Prof: "..... revolutions are not won by enlisting the masses. Revolution is a science only a few are competent to practice. It depends on correct organization and, above all, on communications. Then, at the proper moment in history, they alight. Correctly organized and properly timed it is a bloodless coup. Done clumsily or prematurely and the result is civil war, mob violence, purges, terror. I hope you will forgive me if I say that, up to now, it has been done clumsily."
Wyo looked baffled. "What do you mean by 'correct organization'?"
"Functional organization. How does one design an electric motor? Would you attach a bathtub to it, simply because one was available? Would a bouquet of flowers help? A heap of rocks? No, you would use just those elements necessary to its purpose and make it no larger than needed—and you would incorporate safety factors. Function controls design. "So it is with revolution. Organ must be no larger than necessary—never recruit anyone merely because he wants to join. Nor seek to persuade for the pleasure of having another share your views. He'll share them when the times comes. . . or you've misjudged the moment in history. Oh, there will be an educational organization, but it must be separate; agitprop is no part of basic structure.
"As to basic structure, a revolution starts as a conspiracy therefore structure is small, secret, and organized as to minimize damage by betrayal—since there always are betrayals. One solution is the cell system and so far nothing better has been invented.
"Much theorizing has gone into optimum cell size. I think that history shows that a cell of three is best—more than three can't agree on when to have dinner, much less when to strike.
"Here is a cells-of-three tree. If I were planning to take over Luna. I would start with an three. One would be opted as chairman. We wouldn't vote; choice would be obvious—or we aren't the right three. We would know the next nine people, three cells. . . but each would know only one of us."
"Looks like computer diagram—a ternary logic."
"Does it really? At the next level there are two ways of linking: This comrade, second level, knows his cell leader, his two cellmates, and on the third level he knows the three in his subcell—he may or may not know his cellmates' subcells. One method doubles security, the other doubles speed—of repair if security is penetrated Let's say he does not know his cellmates' subcells—Manuel, how many can he betray? Don't say he won't; today they can brainwash any person, and starch and iron and use him. How many?"
"Six," I answered "His boss, two cellmates, three in sub-cell."
"Seven," Prof corrected, "he betrays himself, too. Which leaves seven broken links on three levels to repair. How?"
"I don't see how it can be," objected Wyoh. "You've got them no split up it falls to pieces."
"Manuel? An exercise for the student" "
"Well ... blokes down here have to have way to send message up three levels. Don't have to know who, just have to know where."
"Precisely!"
_______________________________________________________________
(**) On 7 or 8 December 1970, a coup d'état was allegedly planned in Italy by a combination of military forces, the Sicilian Mafia, and the Masonic Lodge "P2" (propaganda 2). This unholy alliance of subjects failed utterly to carry out the coup, but it is true that there existed a masonic lodge called P2 that collected a large number of high-profile politicians, bankers, professionals, and entrepreneurs. Were they aware that their organization was organizing a coup? And do such organizations still exist today? And, if they exist, how would we know what they are actually doing?